The increasing integration of AI into mental healthcare is transforming how clinical documentation is created. NovoNote, NovoPsych’s AI-powered note-taking assistant, offers mental health professionals an efficient and reliable tool to streamline and automate administrative tasks, saving time and enhancing patient care.
AI tools can be used to ease the note-taking process in different ways, with two common approaches being to record the patient consultation or to dictate notes post-consultation. Both approaches use AI to convert spoken words into written documentation, but differ in their methods and outcomes. It is important to understand the key differences, particularly in relation to how each affects your interactions with patients and privacy considerations.
For example, did you know that using AI for dictation after a consultation to create a summary doesn’t require the same level of patient consent as live recording does? Recording a patient consultation requires explicit consent from the patient, while the clinician dictating into an AI tool after a session does not require the same consent, given the patient is not interacting with the AI tool and the patient’s voice is not being captured.
Integrating AI into your workflow is easier than you might think! Below, we compare the two approaches to help you make an informed choice about which suits your practice best.
Recording Consultations With AI
How does it work?
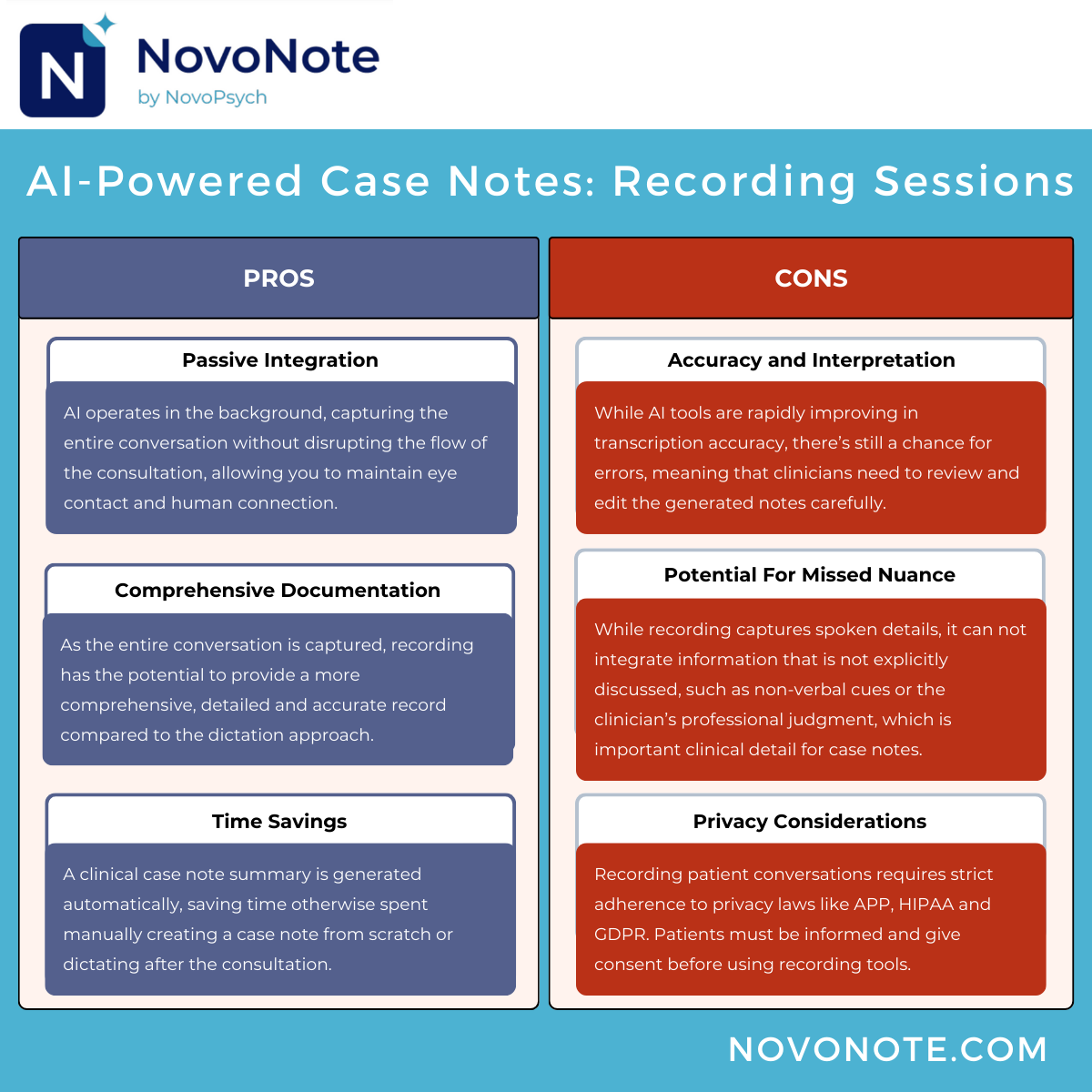
Using the recording method, AI note-taking assistants passively listen to the conversation between the healthcare professional and the patient during the consultation. Using advanced Natural Language Processing (NLP) algorithms, the AI assistant converts the dialogue to a written transcript, identifying key details such as symptoms and treatment plans. The tool then automatically generates a case note summary based on the transcript.
This allows the clinician to focus on the patient without the need to break eye contact or pause for documentation, while still creating accurate, comprehensive records for later review and editing.
When capturing audio from a consultation, practitioners are required to ask for patient consent because the AI tool is directly capturing patient data.
Dictating Notes With AI
How does it work?
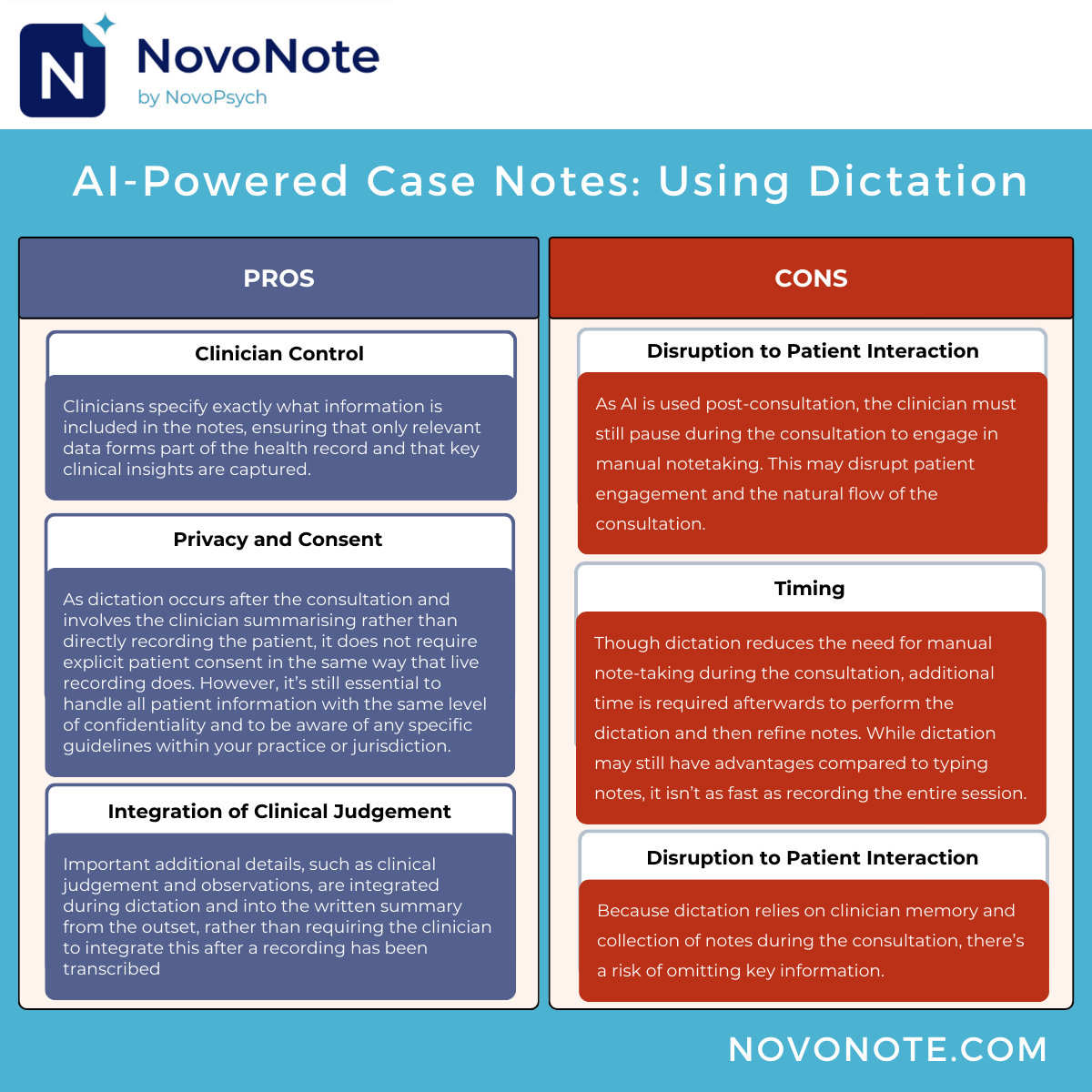
Using an AI assistant for dictation, on the other hand, requires the clinician to actively speak into a microphone or recording device to dictate the content of the patient’s case notes, typically after the consultation has ended.
During the consultation, the practitioner may take notes manually. After the consultation has ended the clinician verbally dictates their notes and any additional information, such as clinical judgement, into the AI note-taking assistant. The AI listens to the clinician’s spoken words, converting them into written text. Unlike recording, which captures the entire conversation, dictation allows the clinician to control the flow of information by specifying what to include in the notes. The dictated content is then transcribed and can be reviewed or edited as needed. This method provides flexibility and control, enabling the clinician to tailor the documentation to their needs and preferences.
Conclusion: Which Method is Right for You?
Both AI-powered recording and dictation offer valuable benefits for mental health professionals looking to streamline their documentation process, but the best method depends on your needs and preferences.
Choose recording if you want a hands-free, passive approach that enables you to focus entirely on patient interaction without being distracted by documentation. This method captures a comprehensive record of the consultation, saving time and ensuring that nothing is missed. However, it requires careful review to ensure accuracy, might not capture every nuance of the conversation, and requires informed patient consent.
Choose dictation if you prefer greater control and flexibility. This approach allows clinicians to dictate exactly what they want to include in the case notes. While it can be more time-consuming and may impact the flow of the consultation, it can work well for those who prefer a more active role in the documentation process and may be easier to integrate into your practice due to differences in patient consent considerations.
Ultimately, the choice comes down to what works best for your practice. Some clinicians may prefer the efficiency of recording, while others may value the customisation that dictation provides. In either case, using AI-assisted note-taking tools responsibly means ensuring privacy, accuracy, and thorough clinical oversight.